USB (Universal Serial Bus) hubs are essential components in the world of computing and electronics, facilitating connectivity and communication between multiple devices and a host computer. Whether you’re looking to connect additional peripherals, charging devices, or expanding your workspace, USB hubs provide a practical solution. This article will delve into the various aspects of USB hubs, including their types, functionality, upstream and downstream ports, Multi-TT architecture, bandwidth considerations, and more.

What is a USB Hub?
A USB hub is a device that expands a single USB port into several ports, allowing multiple devices to connect to a host computer through one single connection. USB hubs come in various forms, including powered and unpowered models, each with its specific use cases and advantages.
1. Types of USB Hubs
- Bus-Powered Hubs: These hubs draw power from the host device and provide limited current to connected devices. They are suitable for low-power devices such as keyboards, mice, and flash drives.
- Powered Hubs: Equipped with their own power supply, powered hubs can provide more significant power output to connected devices. This is particularly useful for charging smartphones, powering external hard drives, and connecting multiple high-power devices simultaneously.
Understanding Ports: Downstream and Upstream
1. Upstream Ports
The upstream port connects the USB hub to the host computer or a primary USB device. This is typically where the hub receives data and power. In a typical setup, the upstream port connects to a USB port on the computer.
2. Downstream Ports
Downstream ports are the connections on the USB hub that allow you to connect various peripherals, such as mice, keyboards, printers, and external drives. The number of downstream ports can vary based on the hub’s design, with some offering as few as two and others providing up to ten or more ports.
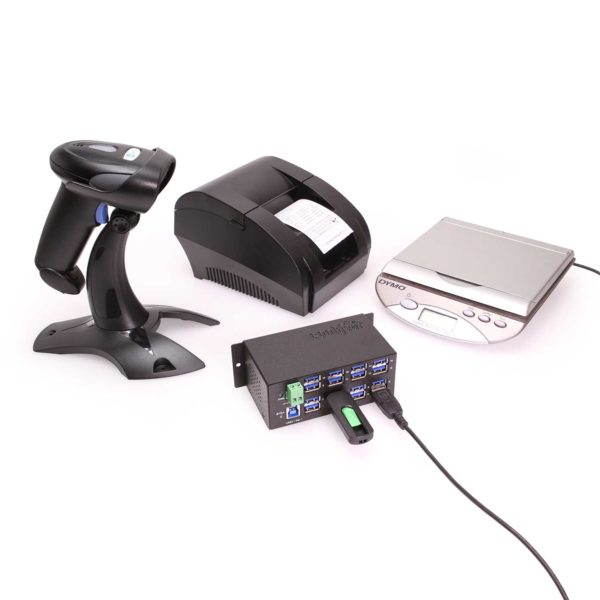 Multi-TT Architecture
Multi-TT Architecture
Multi-TT (Multi-Transaction Translator) architecture is a key feature of modern USB hubs, enhancing their performance and efficiency.
1. What is Multi-TT?
Multi-TT is a technology that allows USB hubs to manage multiple data transfers simultaneously. In traditional USB hubs, all connected devices would share the same bandwidth, which could lead to bottlenecks and slower performance.
- Transaction Translation: With Multi-TT, each downstream port operates as a separate transaction translator, allowing for multiple transactions to occur simultaneously. This means that devices can communicate with the host without waiting for others to finish, improving overall performance.
2. Benefits of Multi-TT
- Improved Performance: By allowing multiple devices to transfer data concurrently, Multi-TT hubs can significantly enhance data throughput.
- Better Device Compatibility: Multi-TT architecture supports a wider range of USB devices, including those with different speed specifications (USB 2.0, USB 3.0, etc.), without compromising performance.
Bandwidth Considerations
1. Understanding USB Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the maximum data transfer rate that a USB connection can support. Different USB standards provide varying bandwidth capabilities:
- USB 2.0: Offers a maximum bandwidth of 480 Mbps.
- USB 3.0 (also known as USB 3.2 Gen 1): Increases the maximum bandwidth to 5 Gbps.
- USB 3.2 Gen 2: Further enhances bandwidth to 10 Gbps.
- USB 3.2 and USB4: Provide even higher data transfer rates, up to 20 Gbps and beyond.
Read our article, Understanding USB Transfer Speeds: A Comprehensive Guide, for more information regarding USB data transfer rates and their history.
2. Bandwidth Distribution in Hubs
When using a USB hub, the total available bandwidth is shared among all connected devices.
- Powered vs. Bus-Powered Hubs: Powered hubs typically have better performance as they can handle higher bandwidth demands due to the additional power supply.
- Single vs. Multi-TT Hubs: Multi-TT hubs can distribute bandwidth more efficiently across connected devices, reducing bottlenecks and ensuring that each device receives sufficient bandwidth for optimal performance.
Additional Features of USB Hubs
1. Charging Capabilities
Many modern USB hubs come with dedicated charging ports that deliver higher power output, suitable for charging smartphones, tablets, and other devices. These ports often use USB Power Delivery (PD) standards, allowing for fast charging capabilities.
2. Data Transfer Speeds
When selecting a USB hub, it’s essential to consider the data transfer speeds supported by both the hub and the connected devices. Ensure that your hub matches the USB version of your devices to achieve optimal performance.
3. Compatibility
USB hubs are generally compatible with a wide range of devices across different operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This versatility makes them valuable for users who work with multiple devices and platforms.
4. LED Indicators
Many USB hubs come with LED indicators that show the power status and data transfer activity, providing users with real-time feedback on their connected devices.
Practical Applications of USB Hubs
USB hubs have become an indispensable tool in various settings, including:

Home Offices: With the rise of remote work, USB hubs facilitate the connection of multiple peripherals such as monitors, keyboards, mice, and printers.

Professional Environments: Designers and engineers often require multiple devices, making hubs essential for connecting tablets, drawing pads, & other equipment.

Gaming Stations: Gamers can connect several devices, including controllers, headsets, and external storage, enhancing their gaming experience.

Educational Settings: In classrooms, USB hubs can connect projectors, document cameras, and student devices, streamlining presentations and collaborative work.
Conclusion
USB hubs play a crucial role in expanding connectivity and enhancing the functionality of modern computing environments. Understanding their components, such as upstream and downstream ports, Multi-TT architecture, and bandwidth considerations, can help users make informed decisions when choosing the right hub for their needs. As technology continues to evolve, USB hubs will remain a key element in ensuring seamless communication between devices, empowering users to maximize their productivity and efficiency.
At Coolgear, we offer a wide range of USB hubs tailored to meet diverse connectivity needs. Explore our products to find the perfect solution for your home or business. Or, learn more about how USB Hubs could be the solution for your next install here.